What is the use of Named Constructor in dart?
In Dart, a named constructor allows you to create multiple ways to instantiate a class by defining additional constructors with meaningful names. This is useful for initializing objects in different ways.
Syntax:
class ClassName{
ClassName.namedConstructorName( ){
// Initialization code
}
}Example:
class Person{
String? name;
int? age;
Person( this.name, this.age );
Person.young( String name ){
this.name = name;
this.age = 18; // Default age for young people
}
void show( ){
print( 'Name: $name, Age: $age' );
}
}
void main( ){
Person p1 = Person( 'Alice', 25 );
p1.show( );
Person p2 = Person.young( 'Bob' );
p2.show( );
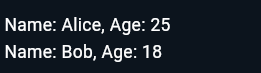
}Output: