How to copy records one table to new table in query?
As an SQL developer, there are many reasons to create a copy of the original table. We have various methods to copy table records, such as importing/exporting records in SQL, and CSV files, or using SQL queries.
This vlog explains how to copy records from one table to a new table in an SQL query.
-- Copy all columns into a new table
SELECT *
INTO newtable [IN externaldb]
FROM oldtable
WHERE condition;
-- Copy only some columns into a new table
SELECT column1, column2, column3, ...
INTO newtable [IN externaldb]
FROM oldtable
WHERE condition;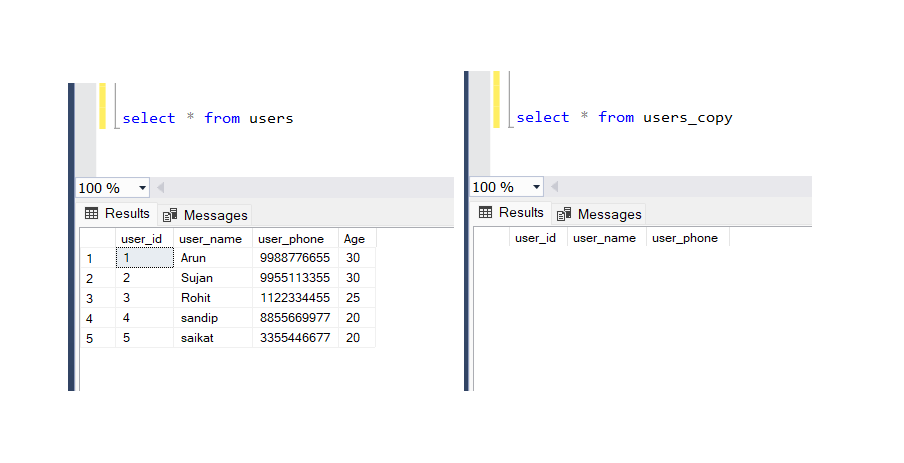
SELECT user_id AS id, user_name AS name, user_phone AS phone
INTO users_copy
FROM users
WHERE age > 20;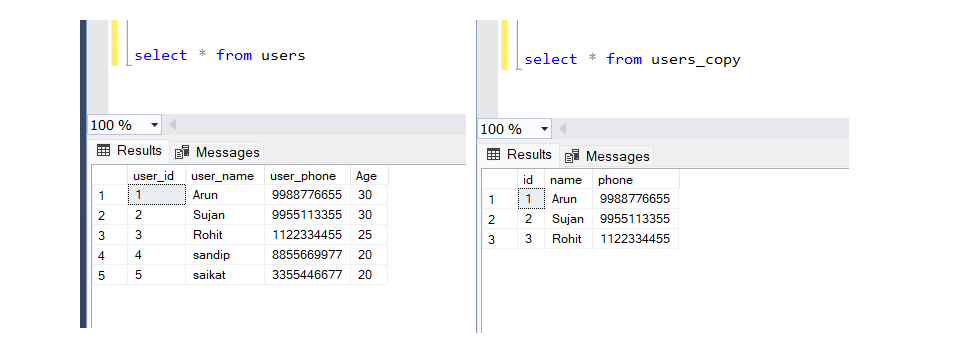
First, we need to write a query and define a new table name, which can also be another database, by using the IN operator. If we use SELECT *, then all field names will be copied as they are. If we want to change the field name, we can do so by defining column name AS new column name. Additionally, we can join more than one table and use the WHERE clause.
SELECT u.user_id AS id,
u.user_name AS name,
u.user_phone AS phone,
a.city,
a.pin
INTO users_address
FROM users AS u
JOIN address AS a ON a.user_id_fk = u.user_id
WHERE u.age > 20;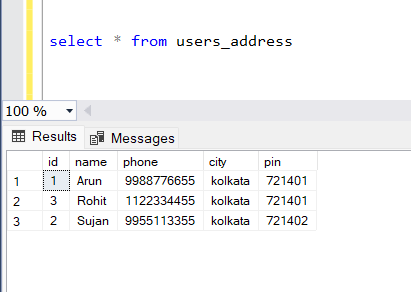
Tip: You can also use SELECT INTO to create a new empty table using the schema of another table. Just add a WHERE clause that causes the query to return no data.
SELECT * INTO newtable
FROM oldtable
WHERE 1 = 0;